

Interpretation of absolute bone conduction test:

When the patient indicates that he no longer hears the sound, the same tuning fork is placed on the mastoid bone of the examiner with ear occlusion same as done in the patient. Now place the vibrating tuning fork on the mastoid bone. Procedure: The patient’s external auditory canal is blocked by the examiner by pressing over the tragus. Absolute Bone Conduction test. In this test, the bone conduction of the patient is compared with that of the examiner presuming that the examiner’s hearing status is normal. It is lateralised to the better ear in sensorineural deafness (as sound travels directly to the cochlea via bone).ģ. Lateralisation: It is lateralised to the worse ear in conductive deafness (this is due to loss of ambient noise or failure to dissipate sound because of the ossicular discontinuity).Normally, it is heard equally in both ears.Ask the patient in which ear, hearing is better. Procedure: Place the vibrating tuning fork in the middle of the forehead/ vertex/ central incisors/ mandibular symphysis from where it will be conducted directly to the cochlea. Weber’s testin conjunction with Rinne’s test helps the clinical diagnosis, especially in unilateral hearing loss. Remember that a negative Rinne for 256, 5 Hz indicates a minimum AB gap of 15, 30, 45 dB, respectively.Ģ. A Rinne negative for all the three tuning forks of 256, 5 Hz indicates an air-bone gap of 45–60 dB.A Rinne test negative for 256 and 512 Hz but positive for 1024 Hz indicates an air-bone gap of 30–45 dB.A Rinne test equal or negative for 256 Hz but positive for 512 Hz indicates an air-bone gap of 20–30 dB.Also, confirmation can be aided by the Weber test which it is lateralized to the better ear.Ī prediction of air-bone gap can be made if tuning forks of 256, 5 Hz are used. To differentiate it from ‘true negative’, the non-test ear is masked with Barany’s noise box while testing for bone conduction. This response is a transcranial transmission of sound to the contralateral healthy ear. The patient is able to perceive the sound of vibrating tuning fork when placed on mastoid but not in front of the ear. Rinne’s false negative is seen in severe unilateral sensorineural hearing loss.It is seen in patients having conductive deafness. It is seen in normal persons or patients having sensorineural deafness. Alternatively, the patient may be asked to compare the loudness of sound heard through air and bone conduction. If he still hears the sound, it means air conduction is more than bone conduction. When the subject indicates that he can’t hear the sound anymore, the tuning fork is brought 25 mm (2.5 cm) in front of external auditory canal, parallel to the acoustic axis. Rinne’s test.The base of a vibrating tuning fork is kept on the mastoid bone of the patient.The clinically useful tuning fork tests include: Thus, BC is a measure of the cochlear function only. The cochlea is stimulated directly by vibrations conducted through the skull bones.
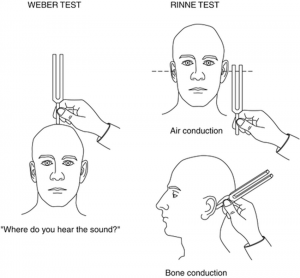
To test bone conduction (BC), the footplate of the vibrating tuning fork is placed firmly on the mastoid bone. Normally, hearing through air conduction is louder and heard twice as long as through the bone conduction route. Thus, by the air conduction test, the function of both the conducting mechanism and the cochlea are tested.

The sound waves are transmitted through the tympanic membrane, middle ear and ossicles to the inner ear. To test air conduction (AC), a vibrating fork is placed vertically in line with the meatus, about 2 cm away from the opening of the external auditory canal.
TUNING FORK TEST VS RINNE FREE
To produce a pure tone, strike the prong at a point 1/3rd of its length from its free end (this will minimize overtones and produce accurate results.).To activate tuning fork, strike it gently against the examiner’s elbow, the heel of the hand or the rubber heel of the shoe.Tuning fork tests Tuning fork tests Tuning fork tests Tuning fork tests Shorter frequency forks are not preferred as they give a sense of bone vibration, while higher frequency forks are not preferred due to their shorter decay time. In clinical practice, tuning fork of 512 Hz is considered ideal (Optimum decay time and produce minimal overtones). Selection of Tuning fork: Tuning forks of varying frequencies such as 128, 256, 512, 1024, 20 hertz are available in the market.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
